Streamlining software development with automated pipelines using Jenkins on AWS

Posted By
Shubham Gaikwad

In the fast-paced world of software development, teams rely on streamlining and automating workflows for efficiency and reliability. Jenkins, a robust automation server, plays a crucial role in the software development lifecycle by enabling teams to automate tasks from building and testing to deployment. This guide will walk you through setting up Jenkins on an AWS EC2 Ubuntu instance and creating a Jenkins pipeline triggered by pushes to a GitHub repository. These steps will empower your development pipeline with seamless integration and automation, fostering a more agile and productive software development environment. Let's dive into the details and unlock Jenkins' full potential in your development workflow.
Why must you use Jenkins?
- Automation prowess: Jenkins excels in automating repetitive tasks, allowing development teams to focus on more complex and creative aspects of their work. By automating build, test, and deployment processes, Jenkins accelerates the delivery pipeline, reducing manual errors and ensuring consistency.
- Extensive plugin ecosystem: Jenkins boasts a vast array of plugins that seamlessly integrate with various tools and technologies. This extensibility makes it adaptable to diverse development environments, enabling teams to tailor Jenkins to their needs.
- Continuous Integration Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Jenkins facilitates CI/CD pipelines, enabling developers to integrate code changes continuously and deploy them automatically. This promotes faster feedback loops, enhances collaboration, and ensures that software is consistently delivered in a production-ready state.
- Scalability and flexibility: Whether working on a small project or managing a large-scale enterprise application, Jenkins scales to meet your needs. Its flexibility allows for customization, making it suitable for various project sizes and complexities.
- Monitoring and reporting: Jenkins provides comprehensive monitoring and reporting capabilities, giving development teams insights into build statuses, test results, and deployment progress. This transparency helps identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement in the development pipeline.
Prerequisites:
- An AWS account. Register here to create a new one.
- An Amazon EC2 key pair. Refer to creating a key pair for steps.
- An AWS IAM user with programmatic key access and permissions to launch EC2 instances.
Steps to set up Jenkins on AWS EC2 instance
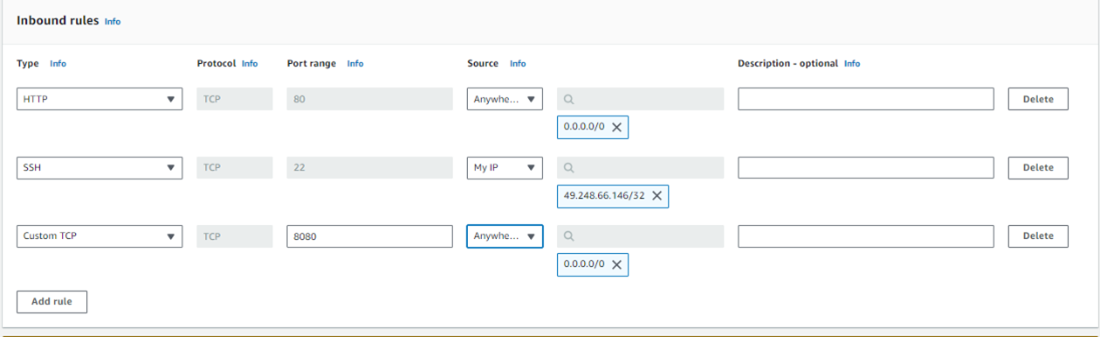
- Step 1: Establish a security group and incorporate the following rules:
- Allow inbound HTTP access from anywhere.
- Allow inbound Secure Shell (SSH) protocol traffic from your computer’s public IP address to facilitate connection with the instance.
- Add a customized TCP Rule permitting traffic on port 8080.
- Step 2: Launch an EC2 instance:
- Launch the EC2 Linux instance as your Jenkins host server. Ensure that the security group associated with the instance allows incoming traffic on the necessary ports by allocating the security group created in the earlier step. When the instance is in a running state, connect to it using Secure Shell (SSH) protocol.
- Step 3: Connect to EC2 instance using SSH:
- Connect to the EC2 instance using SSH, utilizing the key pair associated with it. You can use a Public IPv4 Address or Public IPv4 DNS.
ssh -i your-key.pem ubuntu@your-ec2-public-ip
Here we are following the steps for installing Jenkins on Ubuntu Linux instance, for other eco-systems, you can follow this documentation: Jenkins Installation
- Step 4: Install Java:
- Jenkins relies on Java. Install the Java Development Kit (JDK).
- Execute the following commands to install java on your ec2 instance:
sudo apt update sudo apt install fontconfig openjdk-17-jre
Execute the following command to check if Java is correctly installed:
java -version
- Step 5: Install Jenkins:
- Use following commands to update the package list and proceed to install Jenkins.
sudo wget -O /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins.io-2023.key
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian binary/ | sudo tee \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install jenkins
- Step 6: Start Jenkins Service:
- Initiate the Jenkins Service:
sudo systemctl start jenkins
To ensure that the Jenkins service starts automatically on boot, run the following command:
sudo systemctl enable jenkins
Check if Jenkins is active or not with the following command:
sudo systemctl status jenkins
Open your browser and navigate to HTTP://<YOUR-EC2-PUBLIC-IP>:8080. (Replace the placeholder IP with your ec2 instance’s public IP)
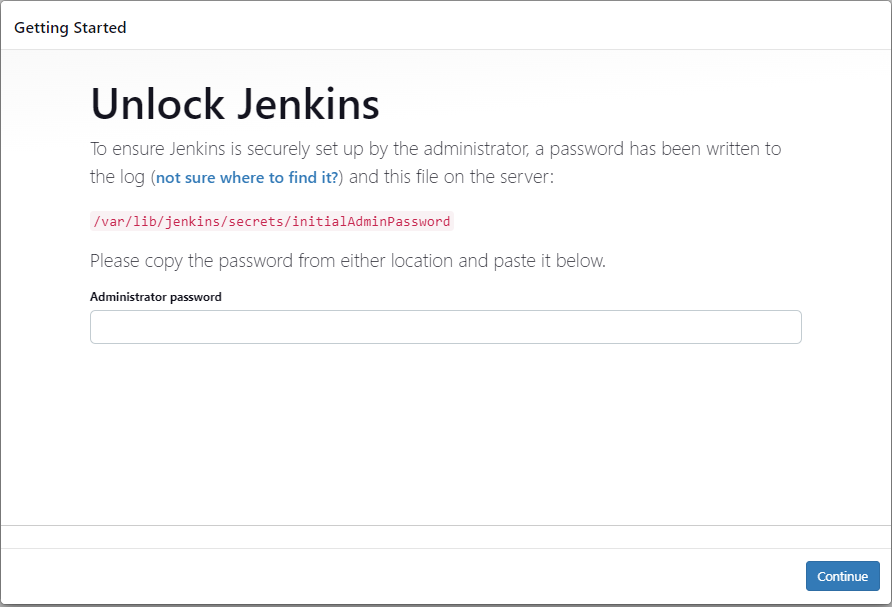
Enter the password found in /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword. You can use the following command:
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
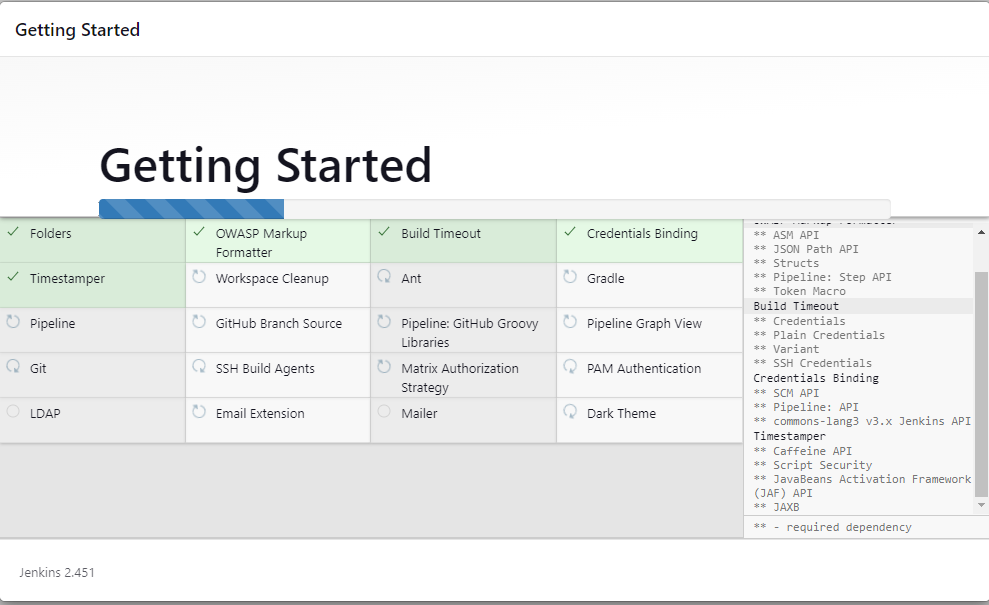
Once signed in you’ll be greeted with the “Getting Started” window. Either choose to install the suggested plugins or install plugins suitable to your needs.
When the installation starts, you’ll see the following window. It might take few seconds to install the plugins.
Once the installation is finished, you’ll be prompted to create your first admin user. You can skip this step to use the default admin user created by Jenkins.
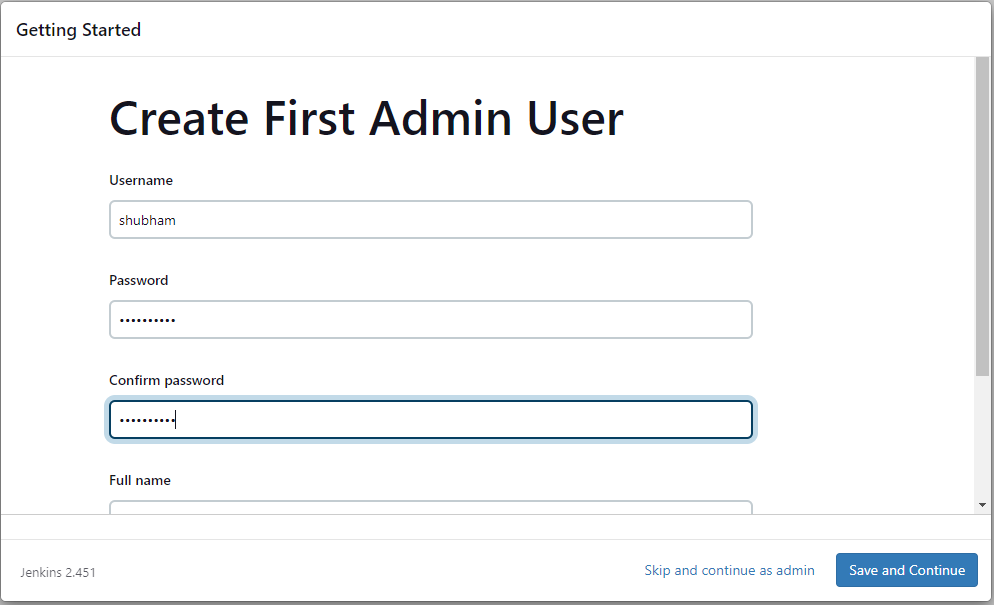
- Step 7: Put your ec2 instance address as the Jenkins URL: HTTP://<YOUR-EC2-PUBLIC-IP>:8080
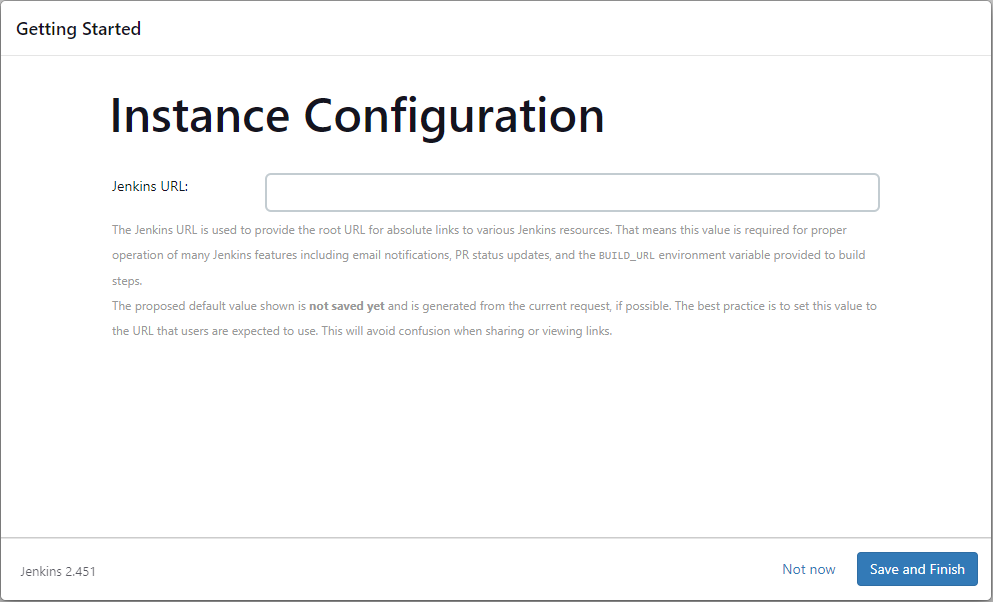
Once you continue, you’ll be on the Jenkins Dashboard.
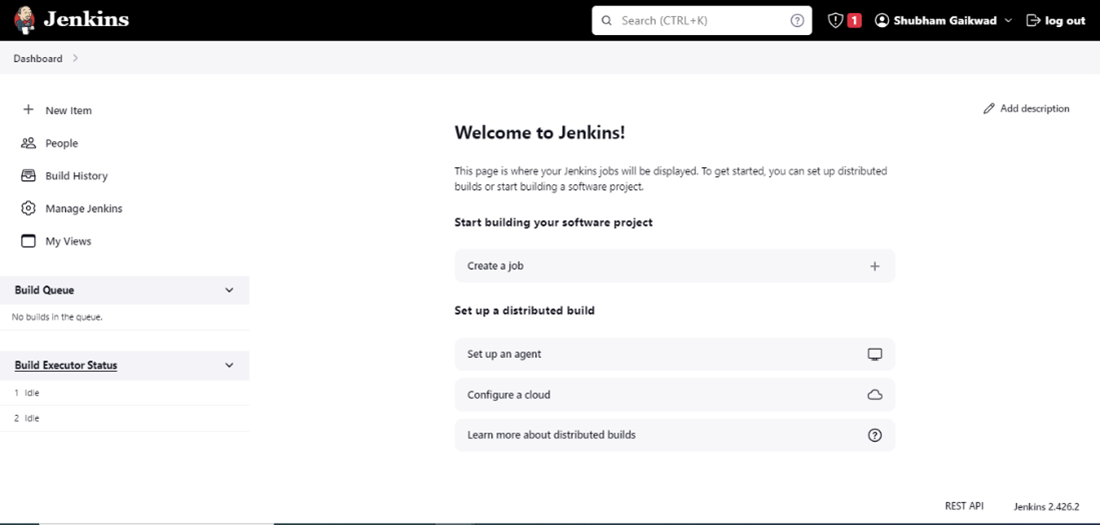
Steps to configure GitHub repository
In your GitHub repository, click on ‘Settings’. I am using my demo git repository for this:
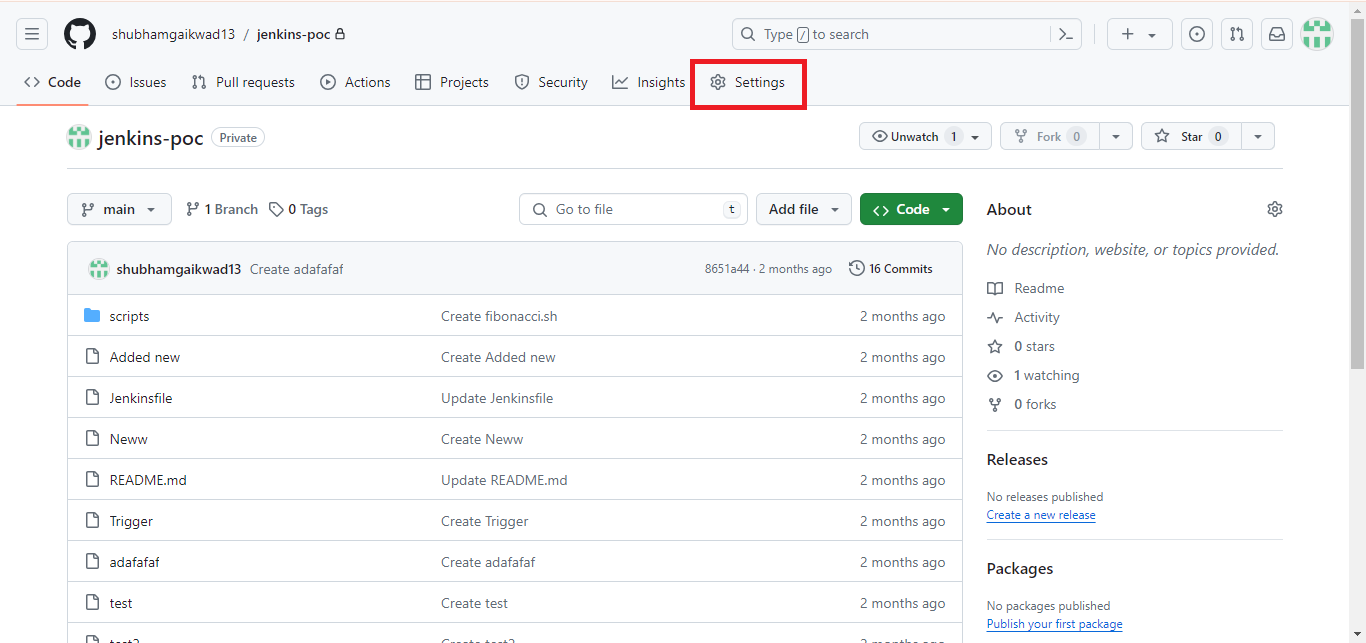
- Step 1: Click on Webhooks and choose ‘Add webhook.’
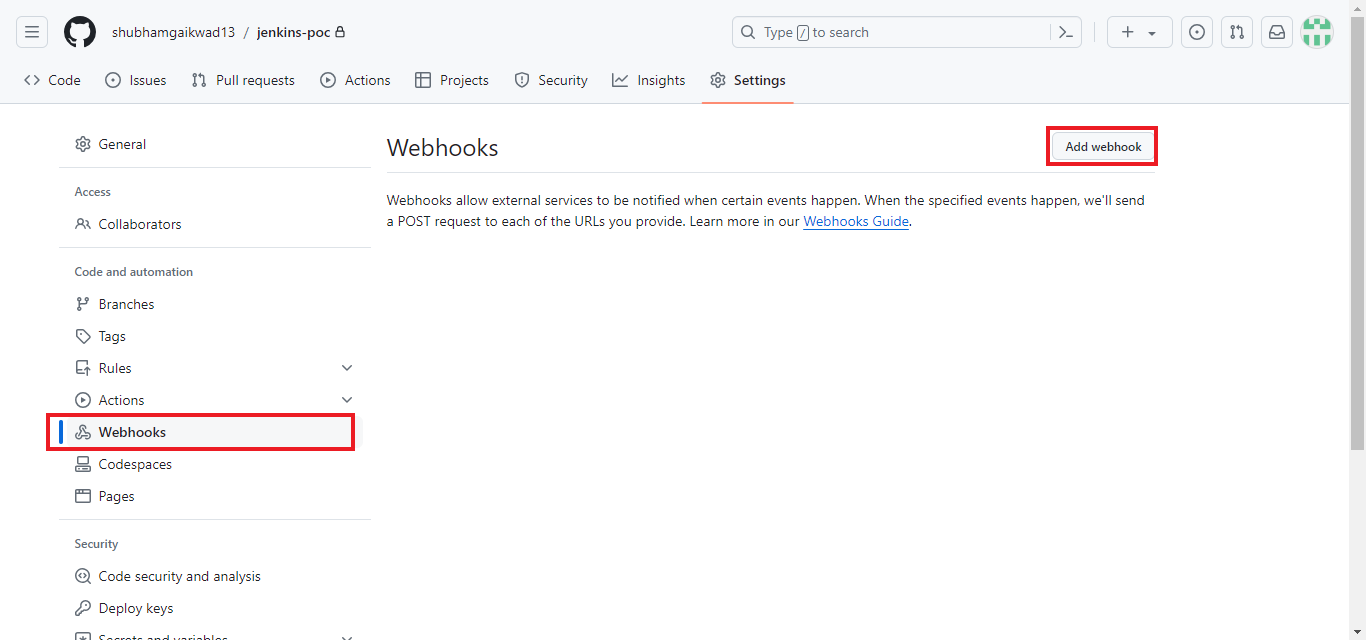
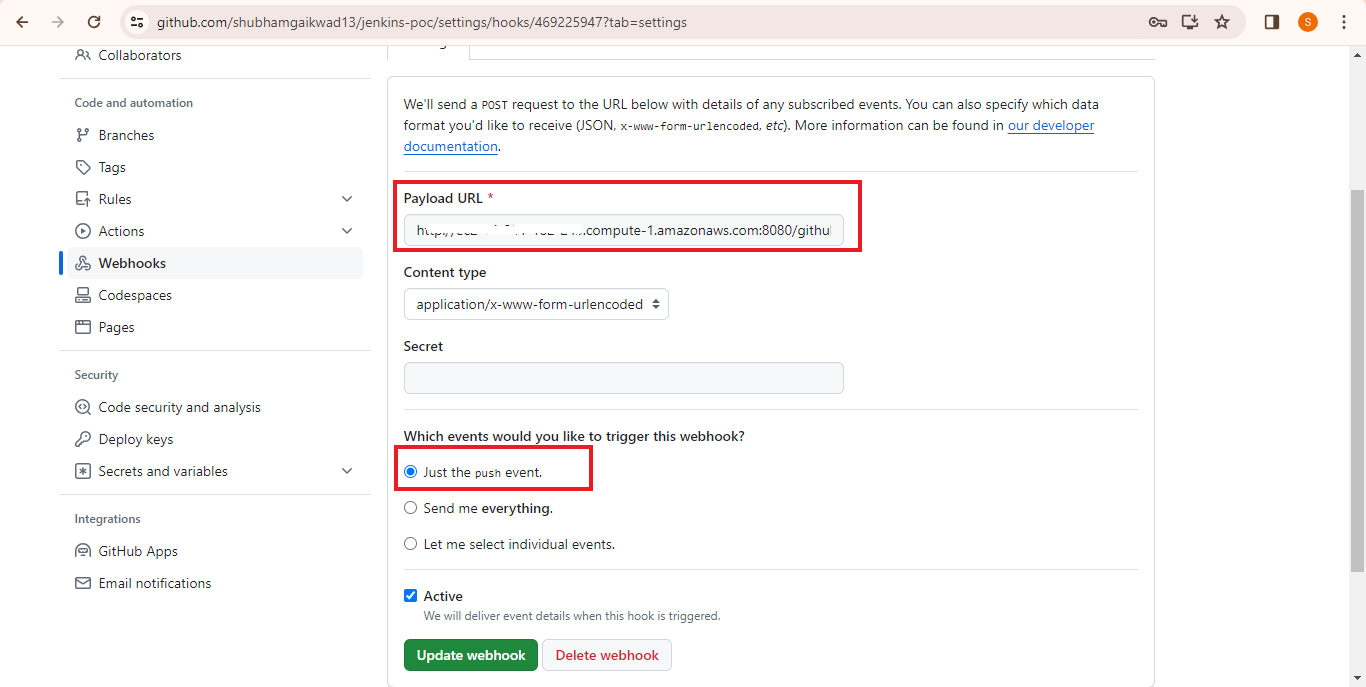
- Step 2: Add your payload URL as: HTTP://<YOUR-EC2-PUBLIC-IP>:8080/GITHUB-WEBHOOK/
- Step 3: Select the event that would trigger the webhook. Here I am selecting ‘Just the push event’ option for demo, but you can also select individual events.
- Step 4: Once you have configured the webhook, click on the Add webhook button to create it.
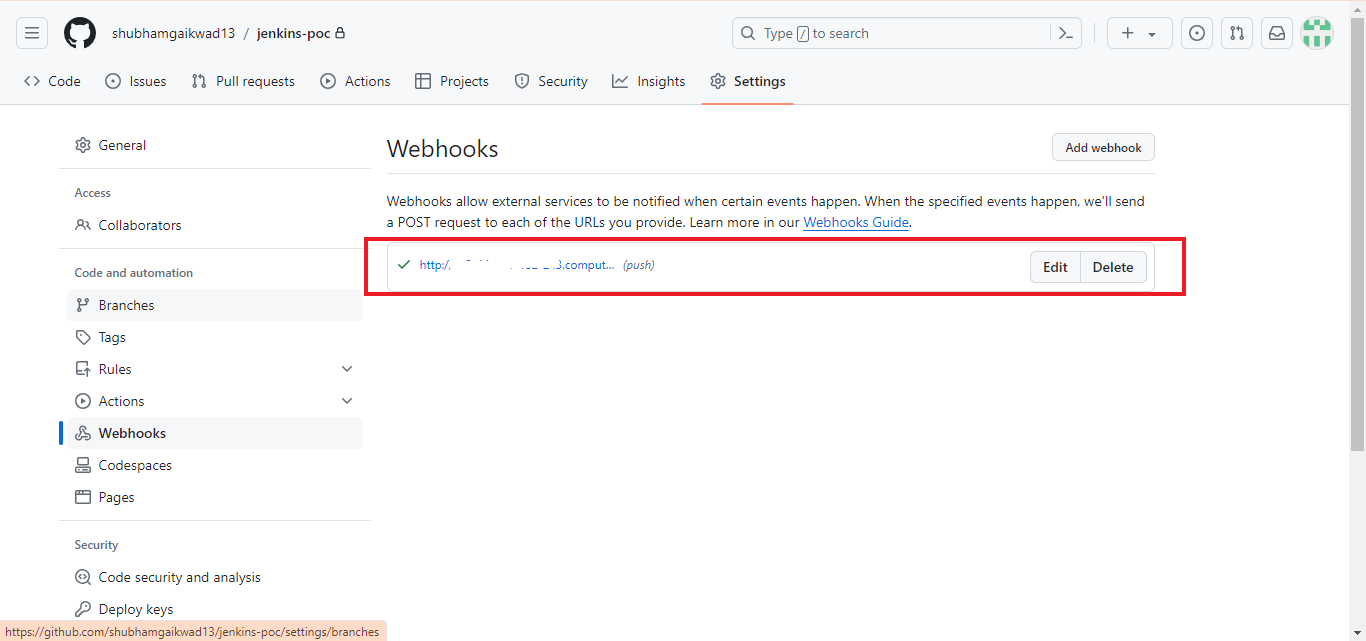
Once you’ve added the webhook, GitHub will ping the payload URL provided. If the request is successful, you will see the green check mark in front of the webhook.
Now let’s go back to our Jenkins Dashboard. To add a pipeline that can be triggered on push event to GitHub repository, we will have to first set up Jenkins to use GitHub.
Steps to create a Jenkins pipeline job:
- Step 1: Click on the + New Item button to create a new pipeline
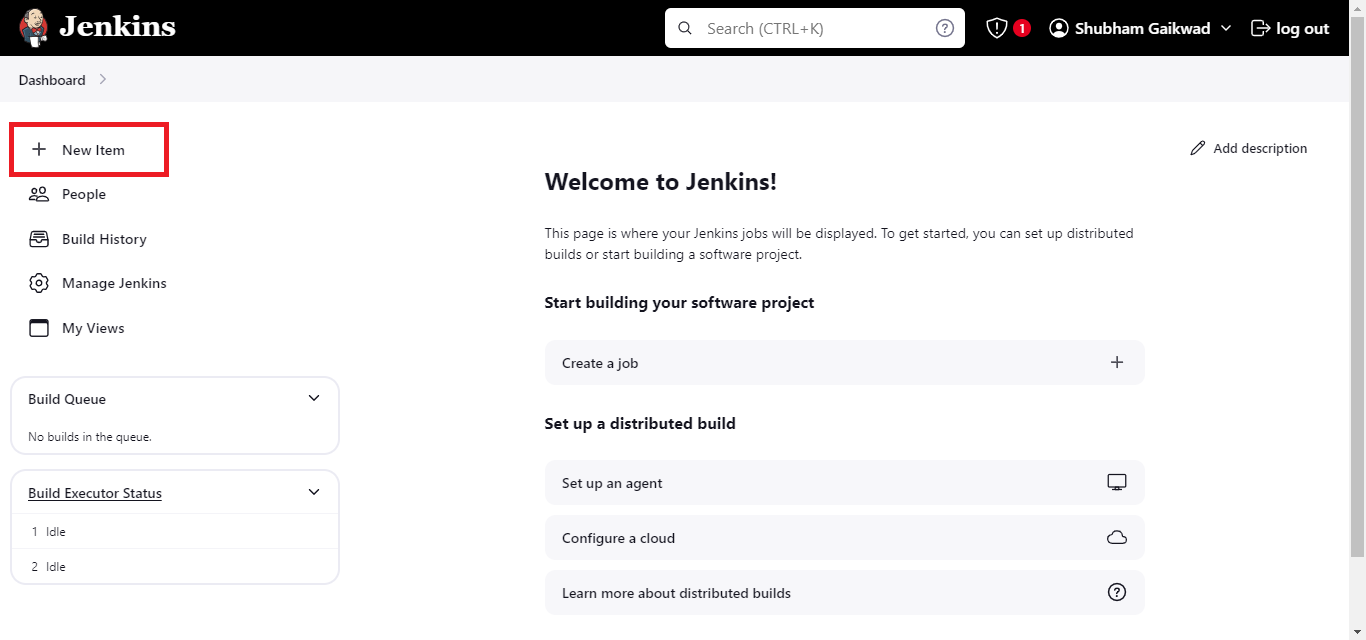
- Step 2: Fill in the name for the pipeline and select the Pipeline option.
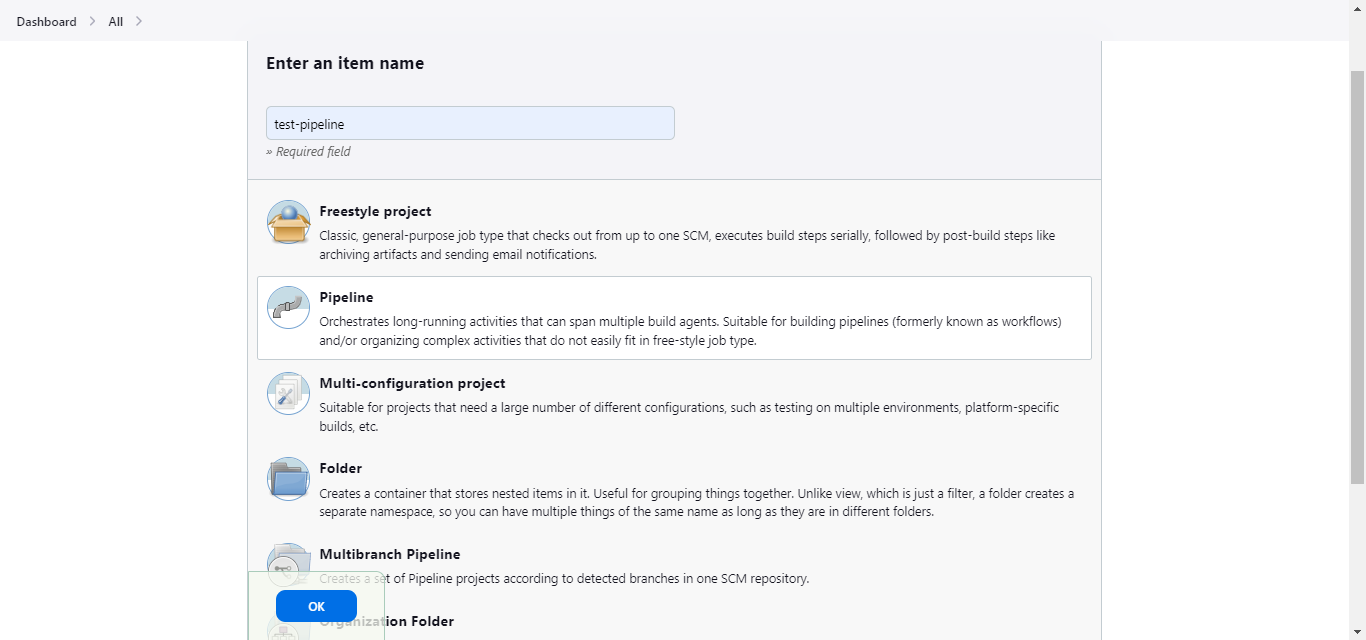
After creating the item, you can view the configuration page of the newly created pipeline or navigate to it from the dashboard.
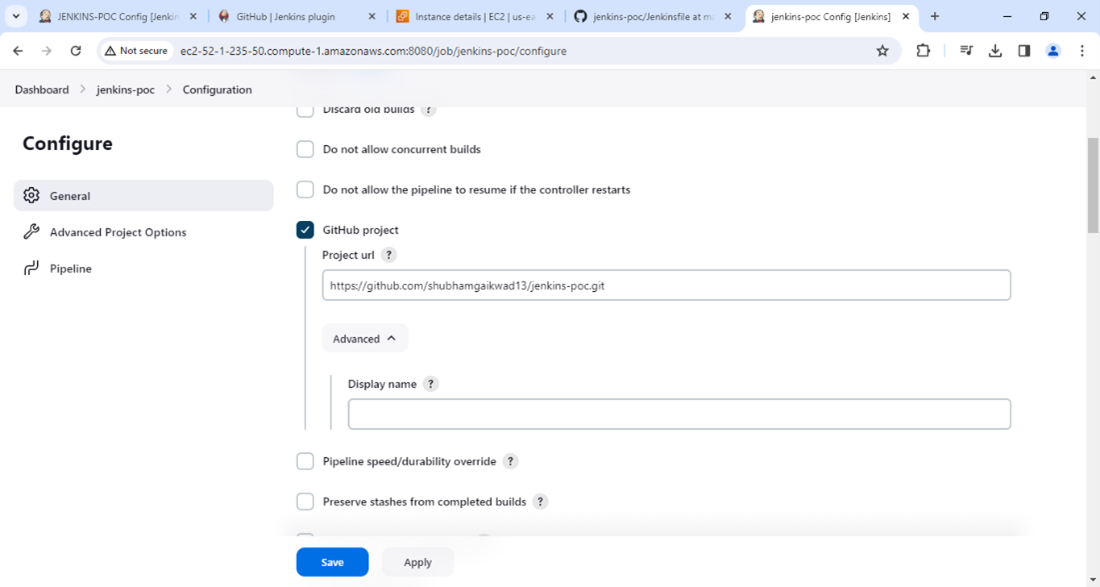
- Step 3: In the configuration section, enable the GitHub project option and add the project's GitHub URL.
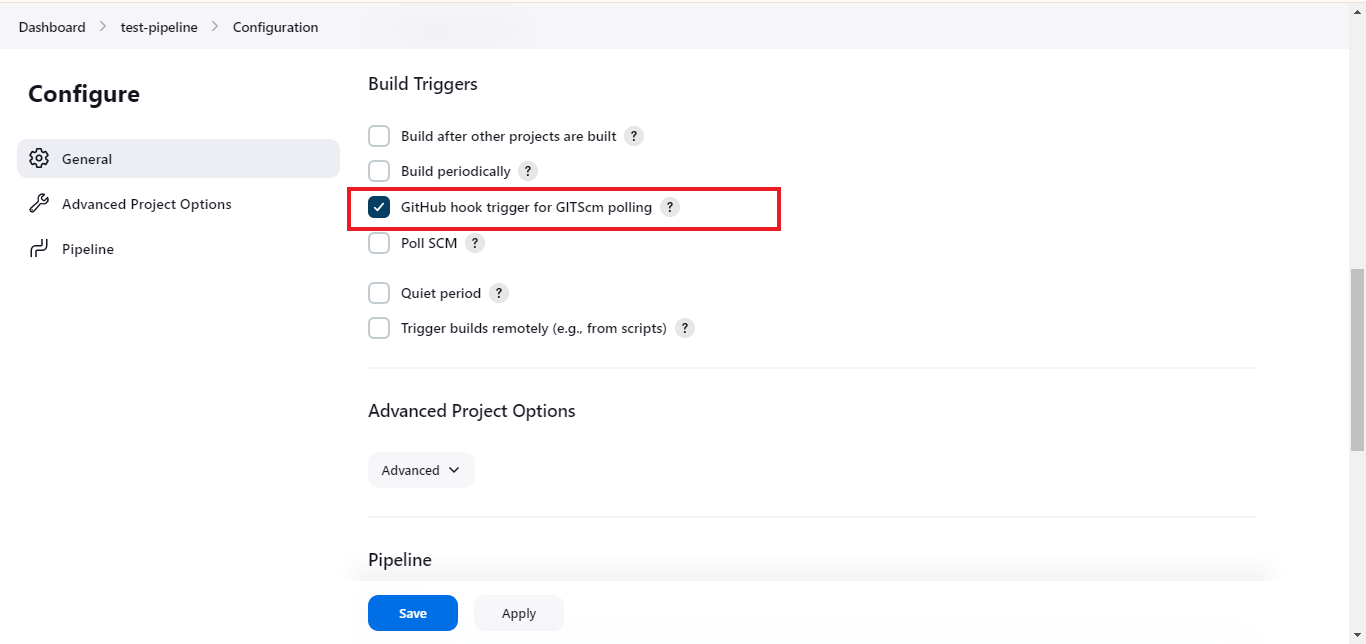
- Step 4: Enable the option GitHub hook trigger for GITScm polling.
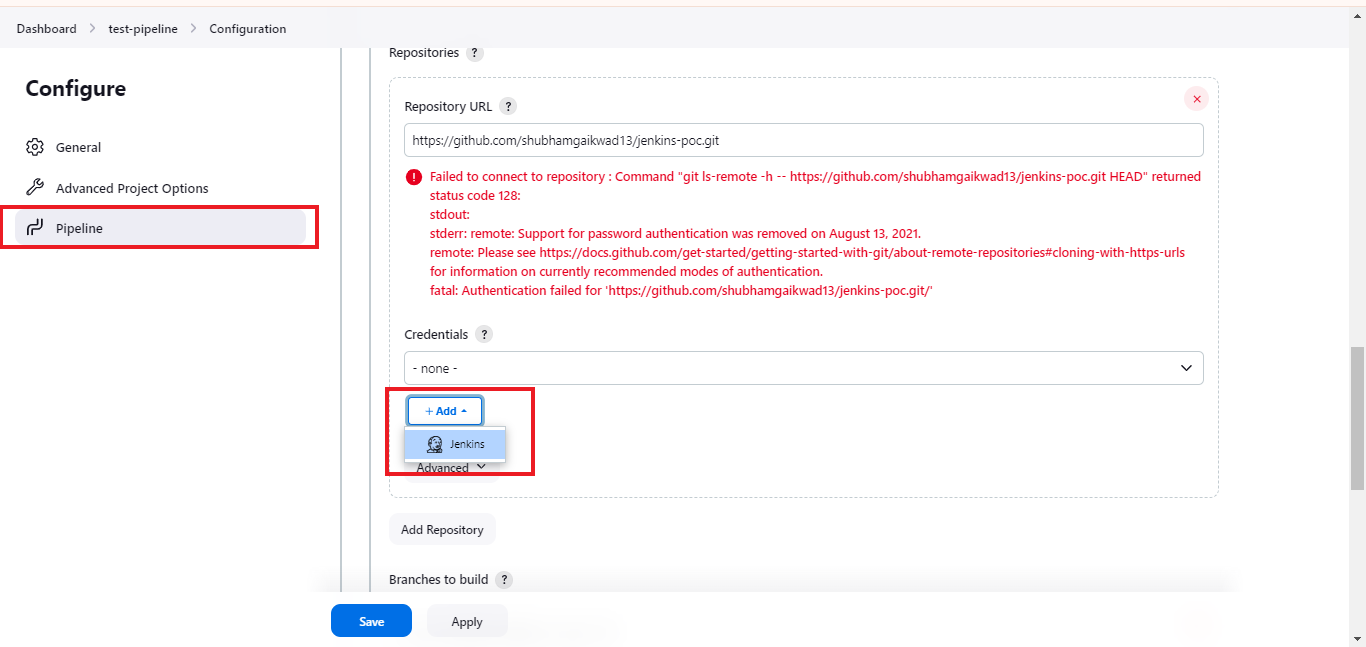
- Step 5: In the pipeline section, choose "Pipeline script from SCM" as the definition and select git as SCM.
- Step 6: Copy your git repository URL to the relevant field.
The error message displayed indicates that Jenkins failed to connect with the repository. This is because we still need to add GitHub credentials. To add your credentials, click on + Add button and select Jenkins
Now, you’ll see the Jenkins Credentials Provider window.
- Step 7: Select the kind of GitHub authentication. Here I have selected the Username with password method.
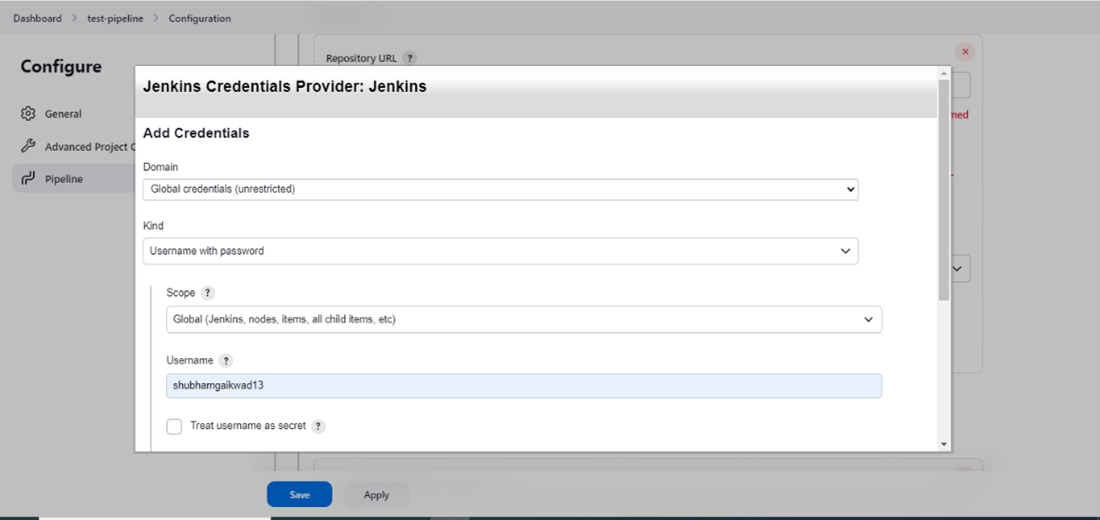
- Step 8: Once you have filled in the details for the selected kind, click on the ‘Add’ button to create credentials.
- Step 9: Now, select the added credentials to authenticate access to your GitHub repository.
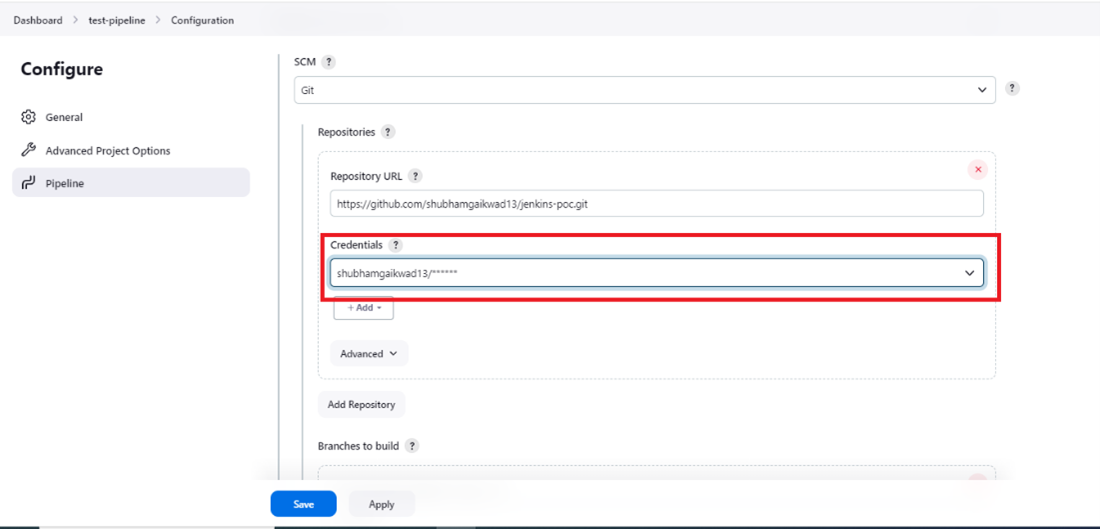
- Step 10: Fill out the branch where you want to trigger the build on push event. Also, fill in the script path for your Jenkinsfile in the repository.
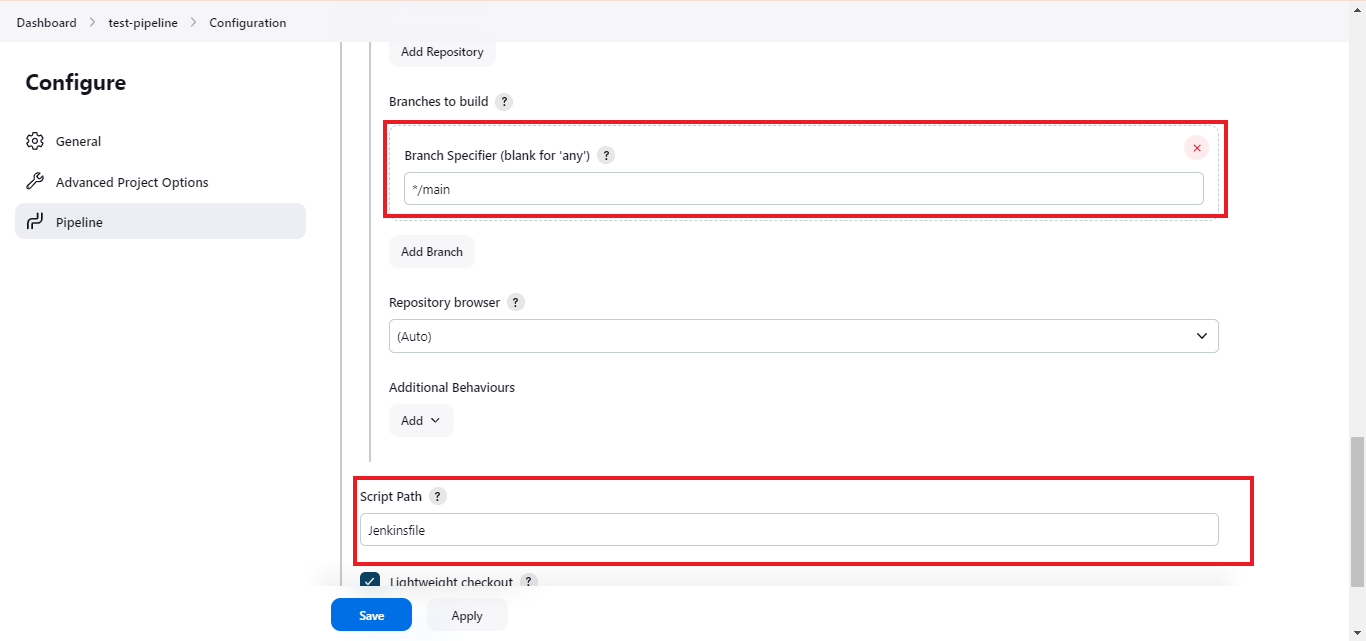
- Step 11: Once you’re done configuring, click on save and apply.
How to trigger a push event on GitHub by adding a file to repository
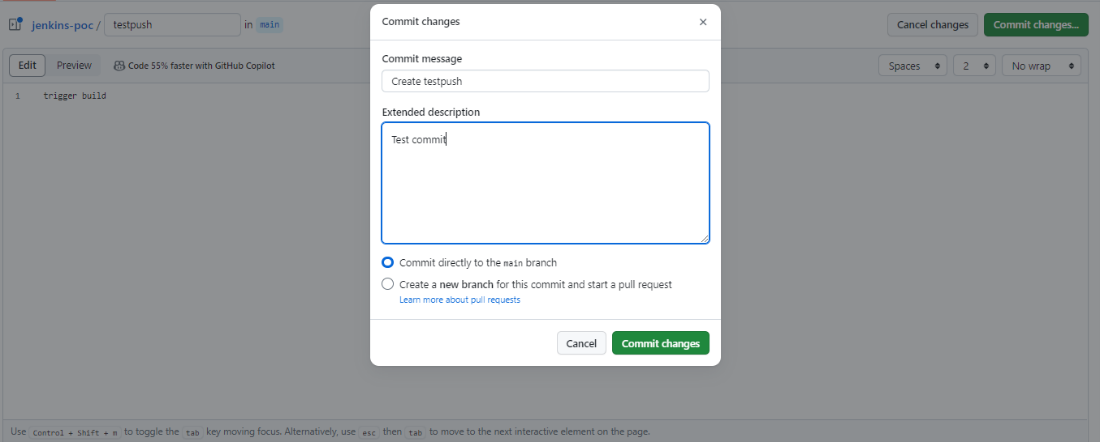
- Step 1: Add a file on GitHub to test the trigger or you can push it from using your preferred method.
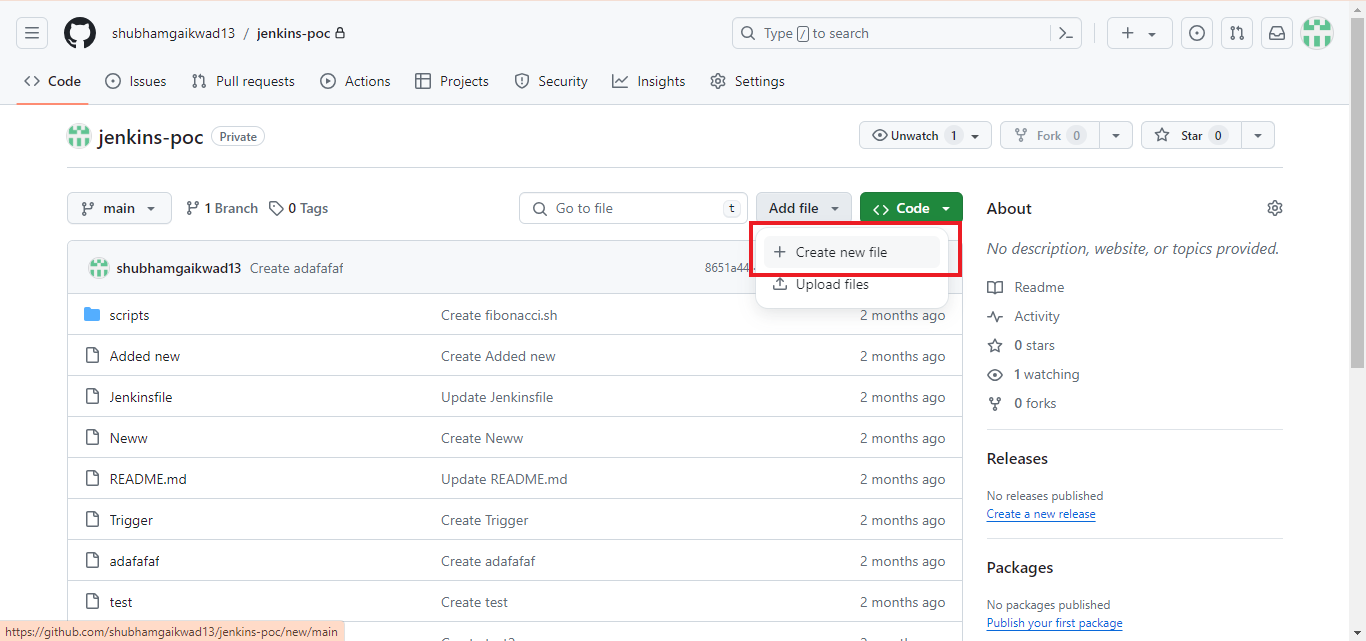
- Step 2: Once the file is added, commit it to the branch you specified in the pipeline configuration.
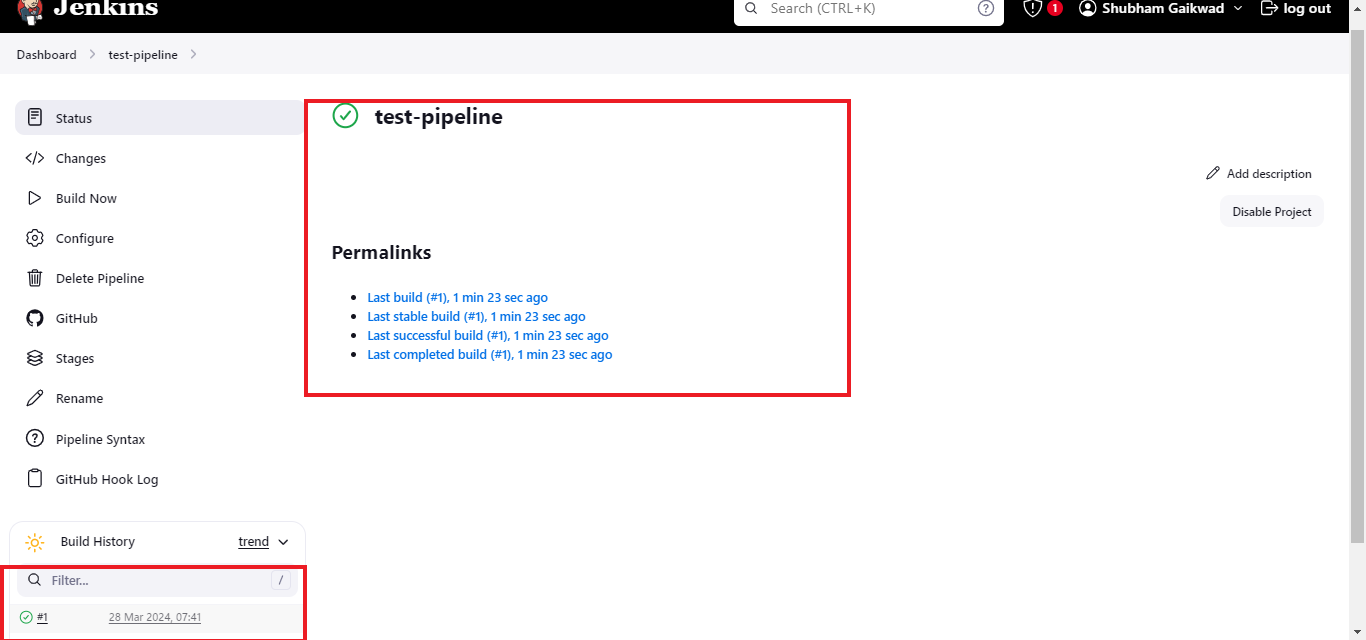
After the commit has been pushed to the repository, and if the Jenkins build is triggered successfully, you’ll see it on that Jenkins job’s page.
Automate your pipeline with Jenkins today
In today's fast-paced world of software development, efficiency and reliability are key. Jenkins is a trustworthy ally that streamlines tasks from building to deployment, making our lives easier. With this guide, you've got everything you need to make Jenkins work its best on AWS. Try it out today and see how it makes your work easier. Embrace the power of automation and take our development process to the next level!
Related Blogs